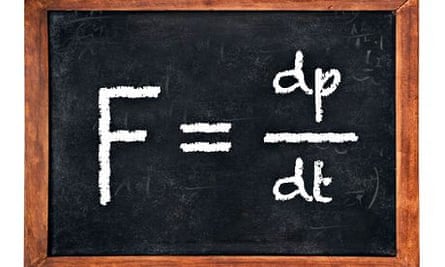Second law of motion the rate of change of momentum is proportional to the imposed force and goes in the direction of the force.
Second law of motion definition in hindi.
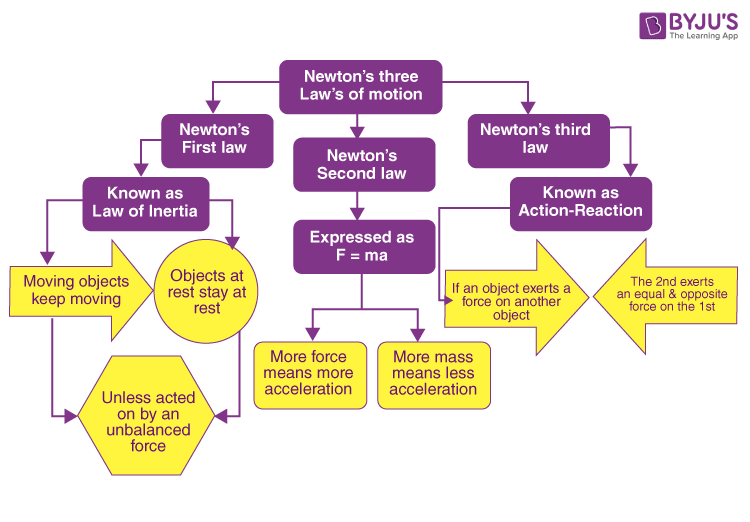
There are three laws of motion enacted by sir isaac ne.
This is the currently selected item.
Newton s second law of motion.
Newton s laws of motion are three physical laws that together laid the foundation for classical mechanics they describe the relationship between a body and the forces acting upon it and its motion in response to those forces.
The larger the mass of the object the greater the force will need to be to cause it to accelerate.
The momentum of a body is equal to the product of its mass and its velocity.
Newton s second law of motion.
More on newton s second law.
More on newton s second law.
The second law of motion describes what happens to the massive body when acted upon by an external force.
Our mission is to provide a free world class education to anyone.
The 2nd law of motion states that the force acting on the body is equal to the product of its mass and acceleration.
Often expressed as the equation a fnet m or rearranged to fnet m a the equation is probably the most important equation in all of mechanics.
It is used to predict how an object will accelerated magnitude and direction in the presence of an unbalanced force.
This law may be written as force mass x acceleration or.
More precisely the first law defines the force qualitatively the second law offers a quantitative measure of the force and the third asserts that a single isolated.
In this physics video in hindi for class 9 and class 11 we discussed on newton s second law of motion.
What is newton s second law.
It states that the time rate of change of the momentum of a body is equal in both magnitude and direction to the force imposed on it.
Newton s second law in hindi उद हरण क द व र समझ.
Newton s second law of motion states that when a force acts on an object it will cause the object to accelerate.
Normal force and contact force.
This is probably why they.
Newton s third law of motion.
The second law shows that the amount of force needed to place an object in motion or to make it change positions relates to its mass and the acceleration of the object.